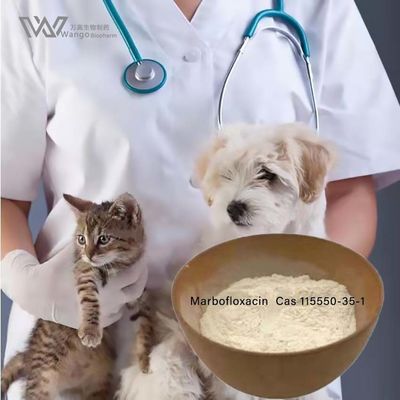
Property: Light Yellow Crystalline Powder,New type of animal dedicated fluoroquinolone drugs. Marbofloxacin is a new type of fluoroquinolone antibiotic, by inhibiting bacterial DNA transcription to inhibit the growth of bacteria, the gram-negative bacteria, gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma have antibacterial activity. Ma Bo effect through oral and injected drugs were able to absorb good, low toxic and side effect.
Pharmacokinetics: absorption was rapid and complete after administration and injection, plasma protein binding rate was low, tissue distribution was wide, and it was well distributed in kidney, liver, lung and skin. The oral bioavailability of pregnant sows and cats was about 80%, and that of calves was more than 100%. All the tissue concentrations detected were higher than those in plasma. Some of them were metabolized into inactive metabolites such as N-demethylation MBF and N-oxygen MBF in the liver. The main excretion pathway was the kidney, and the canine excreted 3045% of the prototype drug in urine. Intramuscular injection and subcutaneous administration of fowl (intramuscular injection), broiler (intramuscular injection), sows (intramuscular injection) were 4.33, 5.265.74 and 10 h, respectively, and the effective blood concentration was maintained for a longer period of time after intramuscular injection and subcutaneous injection, respectively, for 14 h and 13 h.
Application: Fluoroquinolone antibiotic, used for treatment of deep and superficial skin infection, urinary tract infection, the cat's skin and soft tissue infection, acute upper respiratory tract infection. Used for sensitive bacteria caused by cattle, pigs, dogs, cats, respiratory tract, the digestive tract, urinary tract, skin infections, etc. For cattle, sheep mastitis mastitis and pigs - metritis - no milk syndrome are malignant.
Usage :Used for sensitive bacteria caused by cattle, pigs, dogs, cats, respiratory tract, the digestive tract, urinary tract, skin infections, etc. For cattle, sheep mastitis mastitis and pigs - metritis - no milk syndrome are malignant.
Table 1: Mean pharmacokinetic parameters following intravenous administration of marbofloxacin to 6 adult beagle dogs at a dosage of 2.5 mg/lb.
|
Parameter
|
Estimate ± SD* n=6
|
|
Total body clearance, (mL/h•kg)
|
94 ± 8
|
|
Volume of distribution at steady state, Vss, (L/kg)
|
1.19 ± 0.08
|
|
AUC0-inf (μg•h/mL)
|
59 ± 5
|
|
Terminal plasma elimination half-life, t1/2(h)
|
9.5 ± 0.7
|
* SD = standard deviation
Table 2: Mean pharmacokinetic parameters following oral administration of marbofloxacin tablets to adult beagle dogs at a nominal dosage of 1.25 mg/lb or
2.5 mg/lb and to cats at 2.5 mg/lb.†
|
Parameters
|
Dog Estimate ± SD* (1.25 mg/lb) n=6
|
Dog Estimate ± SD* (2.5 mg/lb) n=6
|
Cat Estimate ± SD* (2.5 mg/lb) n=7
|
|
Time of maximum concentration, Tmax(h)
|
1.5 ± 0.3
|
1.8 ± 0.3
|
1.2 ± 0.6
|
|
Maximum concentration, Cmax, (μg/mL)
|
2.0 ± 0.2
|
4.2 ± 0.5
|
4.8 ± 0.7
|
|
AUC0-inf (μg•h/mL)
|
31.2 ± 1.6
|
64 ± 8
|
70 ± 6
|
|
Terminal plasma elimination half-life, t1/2(h)
|
10.7 ± 1.6
|
10.9 ± 0.6
|
12.7 ± 1.1
|
† mean actual dosages administered to dogs were 1.22 mg/lb and 2.56 mg/lb, respectively, and the mean
actual dosage administered to cats was 2.82 mg/lb.
* SD = standard deviation
Figure 2: Mean plasma concentrations (µg/mL) following single oral administration of marbofloxacin to adult beagle dogs at dosages of 1.25 mg/lb or 2.5 mg/lb.
* See Table 4 in Microbiology section for MIC data.
Figure 3: Mean plasma concentrations (µg/mL) following single oral administration of marbofloxacin to adult cats at a dosage of 2.5 mg/lb.
* See Table 5 in Microbiology section for MIC data.
Table 3a: Tissue distribution following a single oral administration of marbofloxacin tablets to adult beagle dogs at a dosage of 1.25 mg/lb*.
|
Tissue
|
Marbofloxacin 2 hours (n=4)
|
Concentrations 18 hours (n=4)
|
(μg/g ± SD) 24 hours (n=4)
|
|
bladder
|
4.8 ± 1.1
|
2.6 ± 1.5
|
1.11 ± 0.19
|
|
bone marrow
|
3.1 ± 0.5
|
1.5 ± 1.5
|
0.7 ± 0.2
|
|
feces
|
15 ± 9
|
48 ± 40
|
26 ± 11
|
|
jejunum
|
3.6 ± 0.5
|
1.3 ± 1.0
|
0.7 ± 0.3
|
|
kidney
|
7.1 ±1.7
|
1.4 ± 0.5
|
0.9 ± 0.3
|
|
lung
|
3.0 ± 0.5
|
0.8 ± 0.2
|
0.57 ± 0.19
|
|
lymph node
|
5.5 ± 1.1
|
1.3 ± 0.3
|
1.0 ± 0.3
|
|
muscle
|
4.1 ± 0.3
|
1.0 ± 0.3
|
0.7 ± 0.2
|
|
prostate
|
5.6 ± 1.4
|
1.8 ± 0.6
|
1.1 ± 0.4
|
|
skin
|
1.9 ± 0.6
|
0.41 ± 0.13
|
0.32 ± 0.08
|
* SD = standard deviation
Table 3b: Tissue distribution following a single oral administration of marbofloxacin tablets to adult beagle dogs at a dosage of 2.5 mg/lb.
|
Tissue
|
Marbofloxacin 2 hours (n=4)
|
Concentrations 18 hours (n=4)
|
(μg/g ± SD*) 24 hours (n=4)
|
|
bladder
|
12 ± 4
|
6 ± 7
|
1.8 ± 0.4
|
|
bone marrow
|
4.6 ± 1.5
|
1.28 ± 0.13
|
0.9 ± 0.3
|
|
feces
|
18 ± 3
|
52 ± 17
|
47 ± 28
|
|
jejunum
|
7.8 ± 1.1
|
2.0 ± 0.3
|
1.1 ± 0.3
|
|
kidney
|
12.7 ±1.7
|
2.7 ± 0.3
|
1.6 ± 0.2
|
|
lung
|
5.48 ± 0.17
|
1.45 ± 0.19
|
1.0 ± 0.2
|
|
lymph node
|
8.3 ± 0.7
|
2.3 ± 0.5
|
2.03 ± 0.06
|
|
muscle
|
7.5 ± 0.5
|
1.8 ± 0.3
|
1.20 ± 0.12
|
|
prostate
|
11 ± 3
|
2.7 ± 1.0
|
2.0 ± 0.5
|
|
skin
|
3.20 ± 0.33
|
0.705 ± 0.013
|
0.46 ± 0.09
|
* SD = standard deviation
Microbiology
The primary action of fluoroquinolones is to inhibit the bacterial enzyme, DNA gyrase. In susceptible organisms, fluoroquinolones are rapidly bactericidal at relatively low concentrations. Marbofloxacin is bactericidal against a broad range of gram-negative and gram-positive organisms. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of pathogens isolated in clinical field studies performed in the United States were determined using National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) standards, and are shown in Tables 4 and 5.
Table 4. MIC Values* (μg/mL) of marbofloxacin against pathogens isolated from skin, soft tissue and urinary tract infections in dogs enrolled in clinical studies conducted during 1994–1996.
|
Organism
|
No. of Isolates
|
MIC50
|
MIC90
|
MIC Range
|
|
Staphylococcus intermedius
|
135
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.125-2
|
|
Escherichia coli
|
61
|
0.03
|
0.06
|
0.015-2
|
|
Proteus mirabilis
|
35
|
0.06
|
0.125
|
0.03-0.25
|
|
Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus,
(not Group A or Group B)
|
25
|
1
|
2
|
0.5-16
|
|
Streptococcus,
Group D enterococcus
|
16
|
1
|
4
|
0.008-4
|
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
13
|
0.015
|
0.06
|
≤0.008-0.5
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
12
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25-0.5
|
|
Enterococcus faecalis
|
11
|
2
|
2
|
1-4
|
|
Klebsiella pneumonia
|
11
|
0.06
|
0.06
|
0.01-0.06
|
|
Pseudomonas spp.
|
9
|
**
|
**
|
0.06-1
|
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
7
|
**
|
**
|
0.25-1
|
* The correlation between in vitro susceptibility data (MIC) and clinical response has not been
determined.
** MIC50 and MIC90 not calculated due to insufficient number of isolates.
Table 5: MIC Values* (μg/mL) of marbofloxacin against pathogens isolated from
skin and soft tissue infections in cats enrolled in clinical studies conducted in 1995
and 1998.
|
Organism
|
No. of Isolates
|
MIC50
|
MIC90
|
MIC Range
|
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
135
|
0.03
|
0.06
|
≤0.008-0.25
|
|
Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus
|
22
|
1
|
1
|
0.06-1
|
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
21
|
0.25
|
0.5
|
0.125-1
|
|
Corynebacterium spp.
|
14
|
0.5
|
1
|
0.25-2
|
|
Staphylococcus intermedius
|
11
|
0.25
|
0.5
|
0.03-0.5
|
|
Enterococcus faecalis
|
10
|
2.0
|
2.0
|
1.0-2.0
|
|
Escherichia coli
|
10
|
0.03
|
0.03
|
0.015-0.03
|
|
Bacillus spp.
|
10
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.125-0.25
|
STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store below 30°C (86°F).
HOW SUPPLIED
Zeniquin tablets are available in the following strengths of marbofloxacin and bottle sizes:
25 mg scored tablets supplied in bottles that contain 100 or 250 tablets
50 mg scored tablets supplied in bottles that contain 100 or 250 tablets
100 mg scored tablets supplied in a 50 tablet bottle
200 mg scored tablets supplied in a 50 tablet bottle


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 








